APFC Panel :
APFC Panel consists of capacitor panel (Group of capacitor installed at one place or panel).
In the above graph current is lagging
P = √3×V×I× cos¢
I = P÷√3×V×cos¢
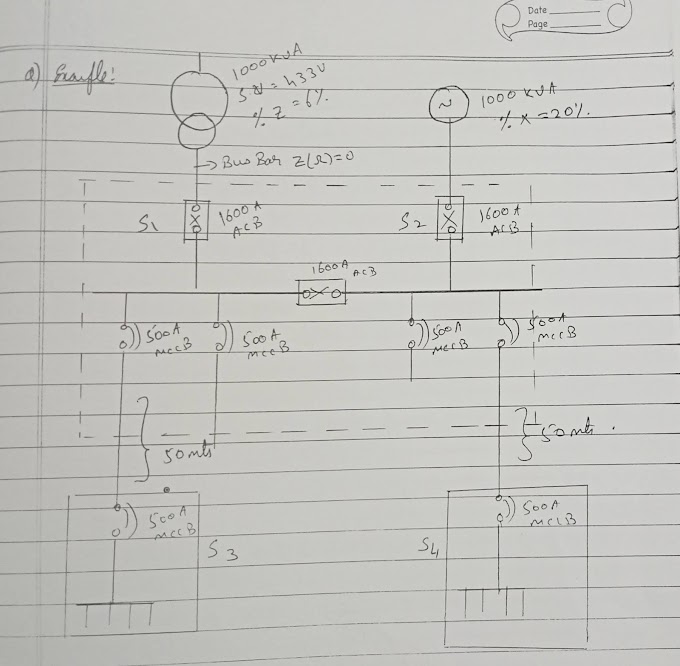
Example :
10KW ; V= 400V
P.F = 0.5 ; I = ?
- I = P ÷ √3×V×cos¢
= 10× 1000/ 1.732× 400×0.5
= 10000/364.4
I = 27.44
I = 28A.
• 10KW ; V= 400V
P.F = 0.95 ; I = ?
- I = P ÷ √3×V×cos¢
= 10× 1000/ 1.732× 400×0.95
= 10000/658.16
I = 15.19
I = 16A.
Therefore,
When P.F increase I (Current) will decrease.
When P.F decrease I (current) will increase.
When P.F decrease V voltage also decrease.
Capacitor available in KVAR rating as their supply reactive power their are rated in 'KVAR'.
Transformer supply both active and reactive power.
If KVAR is '0' (or) cos ¢= 0 then their will be no power supply.
Capacitor take KW and give back KVAR
Relay should know how much rating of the transformer and C.T and capacitor of each rated voltage.
C.T should be installed after the main C.B.
Relay has only 16 points
4 is minimum
16 is maximum.
• APFC control circuit :
- Relay is also having auxiliary supply.
- If relay has AC supply, we have to give to 2 phase.
- If relay has DC supply, we have to give to single phase & Netural.
- CDC →capacitor duty contactor
- From auto 230v supply is given to the relay.
- If any Capacitor should be ON C.T will sense and given the action to the relay where relay NO will become NC to which the capacitor should be ON.
• Inductor :
- Store energy in the form of magnetic field.
- Inductor stop sudden change in current.
- capacitor stop sudden change in voltage.
AC = Reactive (Inductive+Capacitive)
AC = Reactive+Resistance= Impedance
DC = Only Resistance.
Figure :












0 Comments